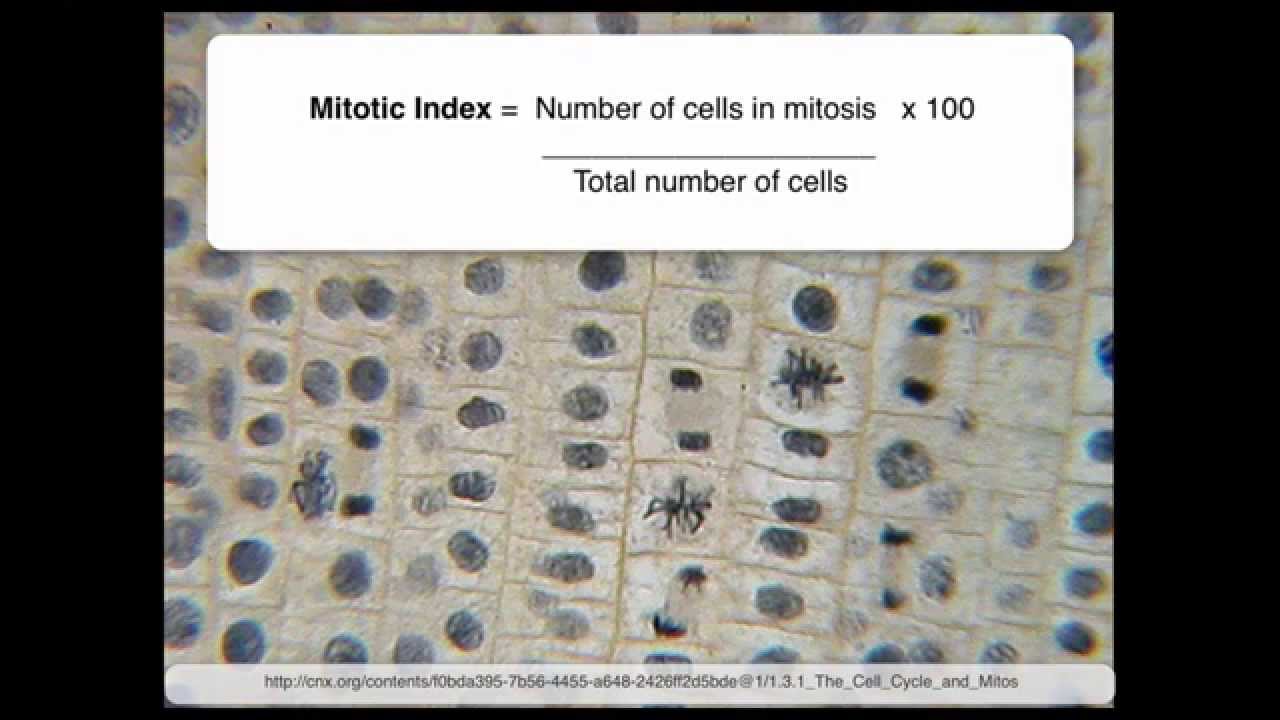
45 mitosis
Quiz: Mitosis - The Biology Corner 4. A cell with 10 chromosomes undergoes mitosis. How many daughter cells are created? ___ Each daughter cell has ___ chromosomes. 2, 10 10, 2 1, 10 2, 20. 5. What structure is responsible for moving the chromosomes during mitosis? nucleolus nuclear membrane spindle cytoplasm. 6. Cytokinesis begins in which phase? metaphase telophase prophase ... Mitosis - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Mitosis is a distinctive cell cycle phase primarily characterized by specific states of chromosome condensation and the formation of the mitotic spindle (mitotic apparatus), a highly complex machinery responsible for chromosome movement, separation of the chromatids, their translocation to the spindle poles, and distribution to the dividing ...
Mitosis | NHGRI - Genome.gov Definición. La mitosis es el proceso por el cual una célula replica sus cromosomas y luego los secreta, produciendo dos núcleos idénticos durante la preparación para la división celular. La mitosis generalmente es seguida por la división igual del contenido de la célula en dos células hijas que tienen genomas idénticos.
Mitosis
Phases of mitosis | Mitosis | Biology (article) | Khan Academy Mitosis consists of four basic phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase). These phases occur in strict sequential order, and cytokinesis - the process of dividing the cell contents to make two new cells - starts ... What is Mitosis? | Stages of Mitosis | Steps of Mitosis | Biology Explorer Mitosis [2] is a type of cell division that involves the production of two daughter cells that have the same genetic makeup like the parent cell. For instance, the cell undergoes a process called the interphase as the preparatory phase before mitosis. Interphase is divided into three major stages: G1, S, and G2 phase. Mitosis - PMC The cellular growth and division cycle. (A) Cartoon of the main segments of the cell cycle.During interphase (G 1, S, G 2), the cell accomplishes sufficient biosynthesis to become two.In mitosis (M), cell parts are reorganized so the mitotic spindle can achieve the equipartition of the chromosomes and centrosomes, leaving the distribution of more numerous components, such as ribosomes, to the ...
Mitosis. Mitosis - Definition, Stages, Function and Purpose | Biology Dictionary Mitosis Definition. Mitosis is the step in the cell cycle that the newly duplicated DNA is separated, and two new cells are formed. This process is important in single-celled eukaryotes, as it is the process of asexual reproduction.In multi-celled eukaryotes, mitosis is how a single zygote can become an entire organism.Mitosis has several distinct stages, or phases, that will be discussed below. Mitosis - Explanation, Features, Satges, Functions and Significance Mitosis is the process of cell division. It is a stage of the cell cycle in which newly formed DNA is separated and two new cells with the same number and type of chromosomes as the parent nucleus are formed. Except for germ cells, most eukaryotic cells divide in such a way that the ploidy or number of chromosomes remains constant. What is Mitosis? | Let's Talk Science And mitosis is an important part of this process. Mitosis creates identical copies of cells. For example, it creates new skin cells to replace dead skin cells. Misconception Alert. Gametes are the cells needed for reproduction. Unlike other cells, they are not produced through mitosis. Instead, sex cells are produced through meiosis. Interactive Mitosis - CELLS alive Interphase. Prophase. Prometaphase. Metaphase. Anaphase. Telophase. Cytokinesis. Interphase
Mitosis (video) | Cell cycle | Khan Academy Video transcript. - In the previous video, we talked about interphase which is the bulk of a cell's life cycle as it grows and its DNA replicates, and it grows some more. And now, we're gonna talk about the actual cell division. We're gonna talk about mitosis. And if you wanna be precise, mitosis is the process by which this one nucleus will ... What Is Mitosis? | Live Science Mitosis is the process by which a cell segregates its duplicated DNA, ultimately dividing its nucleus into two. Cell division is a universal process among living organisms. Mitosis - Science in the News Mitosis is the process of cell division, in which one cell produces two new daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other. Mitosis occurs during development, creating more cells that allow an organism to grow, but it also takes place throughout the lifetime of an organism, as means to replace old cells with new ones. ... The Cell Cycle & Mitosis Tutorial - University of Arizona The Biology Project > Cell Biology > Intro. to Cell Cycle & Mitosis > Problems. The Cell Cycle & Mitosis Tutorial Problem 8: Mitosis Stages The first stage of mitosis when chromosomes start becoming visible in the microscope is called:
Mitosis and the cell cycle - Mitosis and cell specialisation - OCR ... In mitosis, two cells called daughter cells. are produced, each identical to the parent cell. When looking at cells with a microscope, the length of different stages of the cell cycle can be ... Mitosis - College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences Mitosis is the process that facilitates the equal partitioning of replicated chromosomes into two identical groups. Before partitioning can occur, the chromosomes must become aligned so that the separation process can occur in an orderly fashion. The alignment of replicated chromosomes and their separation into two groups is a process that can ... What Is Mitosis? A Complete Guide to Mitotic Cell Division During mitosis, the cell division part of the cell cycle, a single parent cell's replicated genetic material—called chromosomes—divides to produce two new, genetically-identical daughter cells. In the cell cycle, the cell's DNA is replicated in interphase, the phase that precedes mitosis. Mitosis alternates with interphase to make up ... Mitosis - sciencedaily.com Mitosis. In biology, mitosis is the process by which a cell separates its duplicated genome into two identical halves. Note: The above text is excerpted from the Wikipedia article "Mitosis", which ...
Mitosis - PubMed Abstract. SUMMARYAll eukaryotic cells prepare for cell division by forming a "mitotic spindle"-a bipolar machine made from microtubules (MTs) and many associated proteins. This device organizes the already duplicated DNA so one copy of each chromosome attaches to each end of the spindle. Both formation and function of the spindle require ...
Mitosis - Wikipedia The primary result of mitosis and cytokinesis is the transfer of a parent cell's genome into two daughter cells. The genome is composed of a number of chromosomes—complexes of tightly coiled DNA that contain genetic information vital for proper cell function. Because each resultant daughter cell should be genetically identical to the parent cell, the parent cell must make a copy of each ...
Mitosis Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster mitosis: [noun] a process that takes place in the nucleus of a dividing cell, involves typically a series of steps consisting of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, and results in the formation of two new nuclei each having the same number of chromosomes as the parent nucleus — compare meiosis.
National Center for Biotechnology Information National Center for Biotechnology Information
Mitosis in Real Cells - The Biology Corner This is why mitosis is only visible in cells that are dividing, like the whitefish embryo and the onion root tip. Mitosis can take several hours to complete. Scientists will make slides of cells that should be undergoing mitosis in order to find a particular cell in any of the stages - prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase.
What is Mitosis: Significance, Diagram, and Stages - Embibe Yes, Mitosis is the type of cell division that is responsible for the replacement of damaged tissues. The term mitosis was coined by Fleming in \ (1882\). Mitosis occurs in somatic cells and is responsible for the growth, development or repair of tissues and wounds in an organism. Hence it is also known as somatic cell division.
What is mitosis? | Facts | yourgenome.org Facts. Meiosis is a process where a single cell divides twice to produce four cells containing half the original amount of genetic information. These cells are our sex cells - sperm in males, eggs in females. Cells divide and reproduce in two ways, mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis results in two identical daughter cells, whereas meiosis results ...
Mitosis - Genome.gov Mitosis is the process by which a cell replicates its chromosomes and then segregates them, producing two identical nuclei in preparation for cell division. Mitosis is generally followed by equal division of the cell's content into two daughter cells that have identical genomes. YouTube. National Human Genome Research Institute. 34.4K ...
Mitosis Phases in Order | What Are the Stages of Mitosis? - Video ... Mitosis occurs in all of an organism's body cells, also known as somatic cells. Mitosis consists of five phases. The following lists the phases in the correct order: Prophase. Prometaphase ...




Post a Comment for "45 mitosis"